Get your Boob-a-Gram
What is Cancer?
Cancer is a term used for diseases in which abnormal cells divide without control and can invade other tissues. Cancer cells can spread to other parts of the body through the blood and lymph systems.
What is Breast Cancer?
Breast cancer is a disease in which cells in the breast grow  out of control. These cells usually form a tumor that can often be seen on an x-ray or felt as a lump at touch. There are different kinds of breast cancer. The kind of breast cancer depends on which cells in the breast turn into cancer.
out of control. These cells usually form a tumor that can often be seen on an x-ray or felt as a lump at touch. There are different kinds of breast cancer. The kind of breast cancer depends on which cells in the breast turn into cancer.
Breast cancer can begin in different parts of the breast. A breast is made up of three main parts: lobules, ducts, and connective tissue. The lobules are the glands that produce milk. The ducts are tubes that carry milk to the nipple. The connective tissue (which consists of fibrous and fatty tissue) surrounds and holds everything together. Most breast cancers begin in the ducts or lobules.
Breast cancer can spread outside the breast through blood vessels and lymph vessels. When breast cancer spreads to other parts of the body, it is said to have metastasized.
Facts
Afro-descendants get breast cancer less than any race; however Afro-descendants tend to die from the disease at a higher rate. Afro-descendant women are more likely than white women to get a form of breast cancer called “triple-negative breast cancer”, a kind of breast cancer in most cases is aggressive and often comes back after treatment.
Public health agencies are working to make sure all women are screened for breast cancer as recommended, and those who are diagnosed with breast cancer can get the best treatments. They also are helping women reduce the risk factors that raise their chances of getting breast cancer. Together, these efforts could reduce racial disparities in breast cancer
What important to Know? Breast Cancer Screenings
Get you annual mammogram and remember to check your breast every month at the same time each month.
- Women ages 40 to 44 should have the choice to start annual breast cancer screening with mammograms (x-rays of the breast) if they wish to do so.
- Women age 45 to 54 should get mammograms every year.
- Women 55 and older should switch to mammograms every 2 years, or can continue yearly screening.
- Screening should continue as long as a woman is in good health and is expected to live 10 more years or longer.
- All women should be familiar with the known benefits, limitations, and potential harms linked to breast cancer screening.
Mammogram
 A mammogram is an X-ray of the breast. Mammograms are the best way to find breast cancer early, when it is easier to treat and before it is big enough to feel or cause symptoms. Having regular mammograms can lower the risk of dying from breast cancer. At this time, a mammogram is the best way to find breast cancer for most women.
A mammogram is an X-ray of the breast. Mammograms are the best way to find breast cancer early, when it is easier to treat and before it is big enough to feel or cause symptoms. Having regular mammograms can lower the risk of dying from breast cancer. At this time, a mammogram is the best way to find breast cancer for most women.
Breast Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
A breast MRI uses magnets and radio waves to take pictures of the breast. MRI is used along with mammograms to screen women who are at higher risk of getting breast cancer. Because breast MRIs may appear abnormal even when there is no cancer, they are not used for women at average risk.
Clinical Breast Exam
A clinical breast exam is an examination by a doctor or nurse, who uses his or her hands to feel for lumps or other any changes.
Breast Self-Awareness
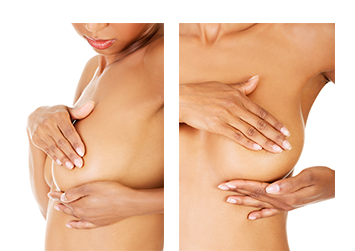 Being familiar with how your breasts look and feel can help you notice symptoms such as lumps, pain, or changes in size that may be of concern. These could include changes found during a breast self-exam. You should report any changes that you notice to your doctor or health care provider.
Being familiar with how your breasts look and feel can help you notice symptoms such as lumps, pain, or changes in size that may be of concern. These could include changes found during a breast self-exam. You should report any changes that you notice to your doctor or health care provider.
Having a clinical breast exam or doing a breast self-exam has not been found to lower the risk of dying from breast cancer.